Pythagorean Theorem
In any right triangle, the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (remember this is the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares whose sides are the two legs (the two sides that meet at a right angle).
The Pythagorean Theorem helps us to figure out the length of the sides of a triangle. If a triangle has a right angle (also called a 90 degree angle) then the following formula holds true.
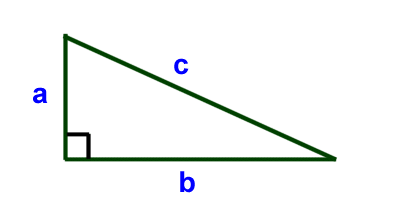
Where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle and c is the side opposite the right angle. In this example, c is also called the hypotenuse.